Overview
• Redshift is based on PostgreSQL, but it’s not used for OLTP • It’s OLAP – online analytical processing (analytics and data warehousing) • 10x better performance than other data warehouses, scale to PBs of data • Columnar storage of data (instead of row based) & parallel query engine • Two modes: Provisioned cluster or Serverless cluster • Has a SQL interface for performing the queries • BI tools such as Amazon Quicksight or Tableau integrate with it • vs Athena: faster queries / joins / aggregations thanks to indexes
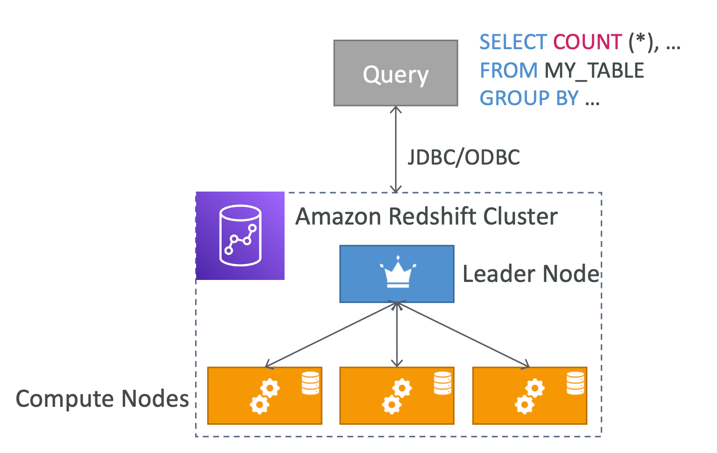
Redshift Cluster
• Leader node: for query planning, results aggregation
• Compute node: for performing the queries, send results to leader
• Provisioned mode:
• Choose instance types in advance
• Can reserve instances for cost savings
Snapshots & DR
• Redshift has “Multi-AZ” mode for some clusters • Snapshots are point-in-time backups of a cluster, stored internally in S3 • Snapshots are incremental (only what has changed is saved) • You can restore a snapshot into a new cluster • Automated: every 8 hours, every 5 GB, or on a schedule. Set retention between | to 35 days • Manual: snapshot is retained until you delete it • You can configure Amazon Redshift to automatically copy snapshots (automated.or manual) of a cluster to another AWS Region
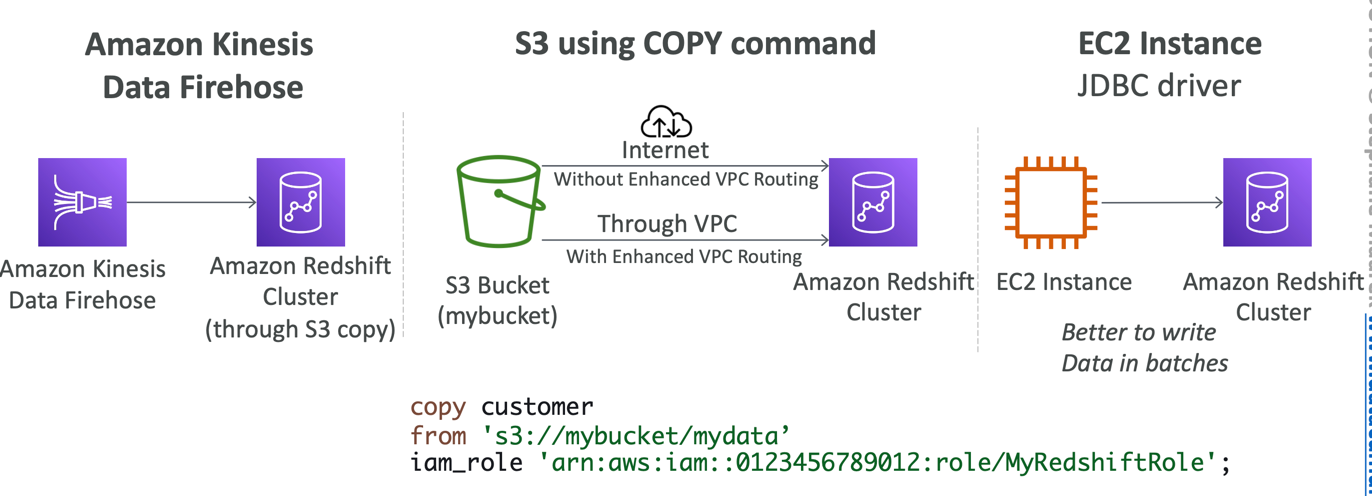
Loading data into Redshift: Large inserts are MUCH better
Redshift Serverless
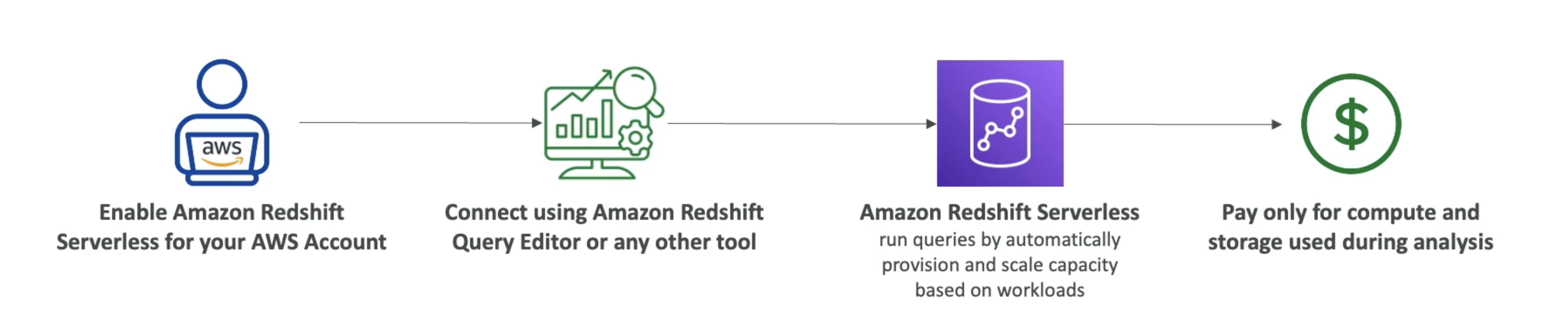
- Automatically provisions and scales data warehouse underlying capacity
- Run analytics workloads without managing data warehouse infrastructure
- Pay only for what you use (save costs)
- Use cases: Reporting, dashboarding applications, real-time analytics...