- Fully Managed Highly available with replication across 3 AZ
- NoSQL database - not a relational database
- Scales to massive workloads, distributed "serverless" database
- Millions of requests per seconds, trillions of row, 100s of TB of storage
- Fast and consistent in performance
- Single-digit millisecond latency - low latency retrieval
- Integrated with IAM for security, authorization and administration
- Low cost and auto scaling capabilities
- Standard & Infrequent Access (IA) Table Class
DynamoDB - Basics
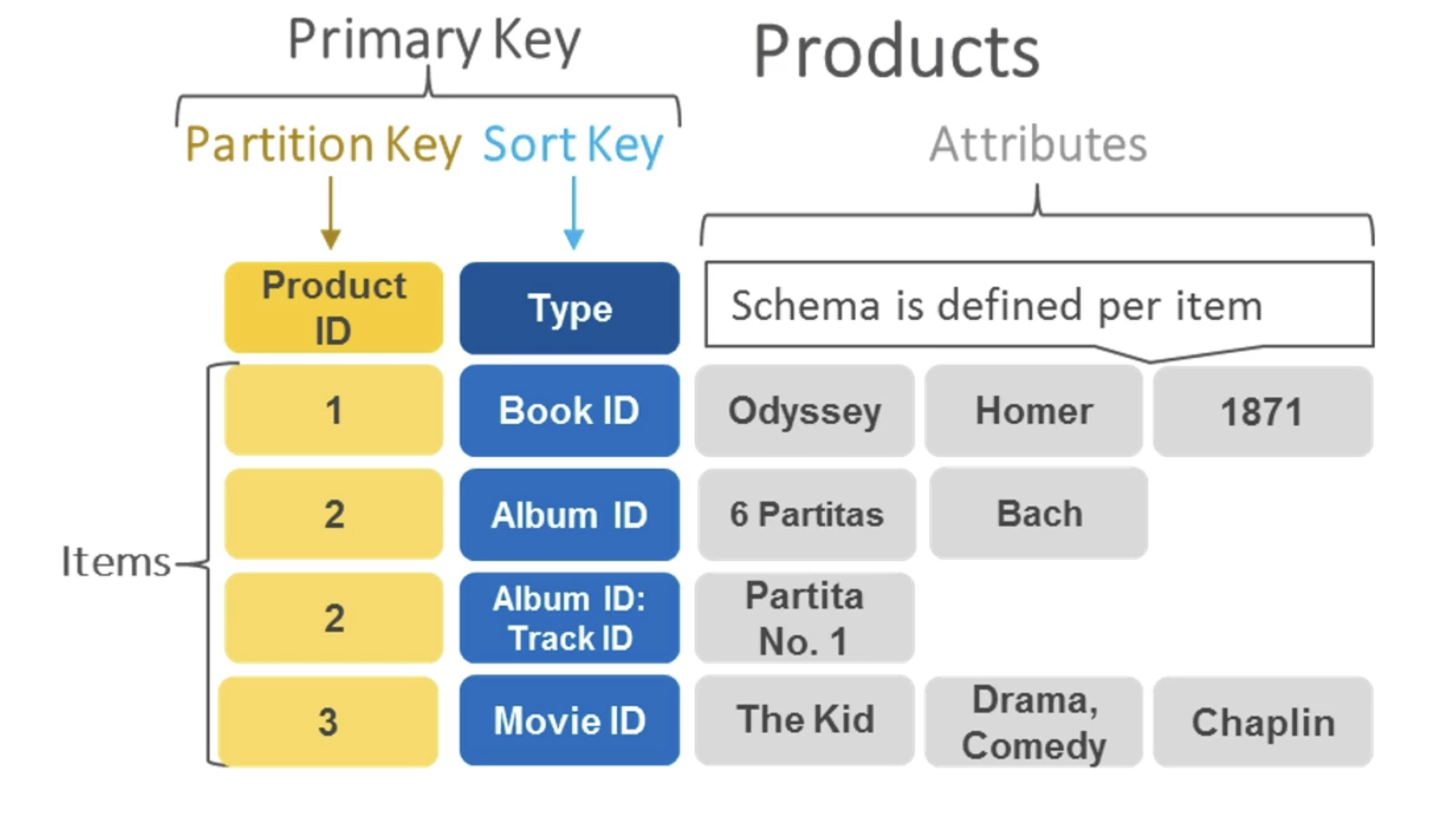
- DynamoDB is made of Tables
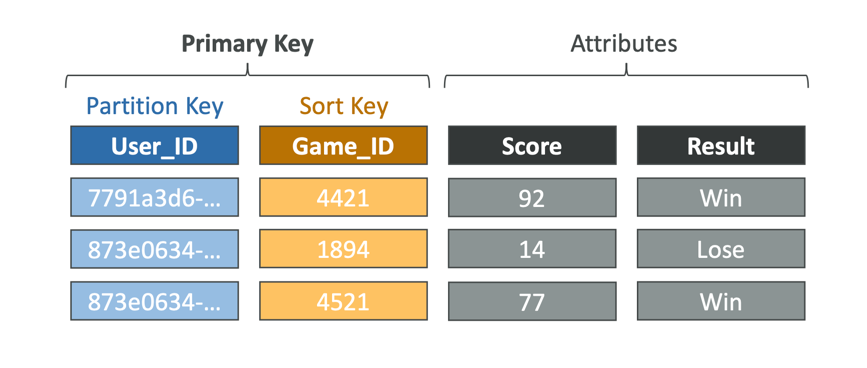
- Each table has a Primary Key (must be decided at creation time)
- Each table can have an infinite number of items (= rows)
- Each item has attributes (can be added over time – can be null)
- Maximum size of an item is 400KB
- Data types supported are:
- Scalar Types – String, Number, Binary, Boolean, Null
- Document Types – List, Map
- Set Types – String Set, Number Set, Binary Set
- Therefore, in DynamoDB you can rapidly evolve schemas
DynamoDB – Read/Write Capacity Modes
- Control how you manage your table’s capacity (read/write throughput)
Provisioned Mode (default)
- You specify the number of reads/writes per second
- You need to plan capacity beforehand
- Pay for provisioned Read Capacity Units (RCU) & Write Capacity Units (WCU)
- Possibility to add auto-scaling mode for RCU & WCU
On-Demand Mode
- Read/writes automatically scale up/down with your workloads
- No capacity planning needed
- Pay for what you use, more expensive ($$$)
- Great for unpredictable workloads, steep sudden spikes
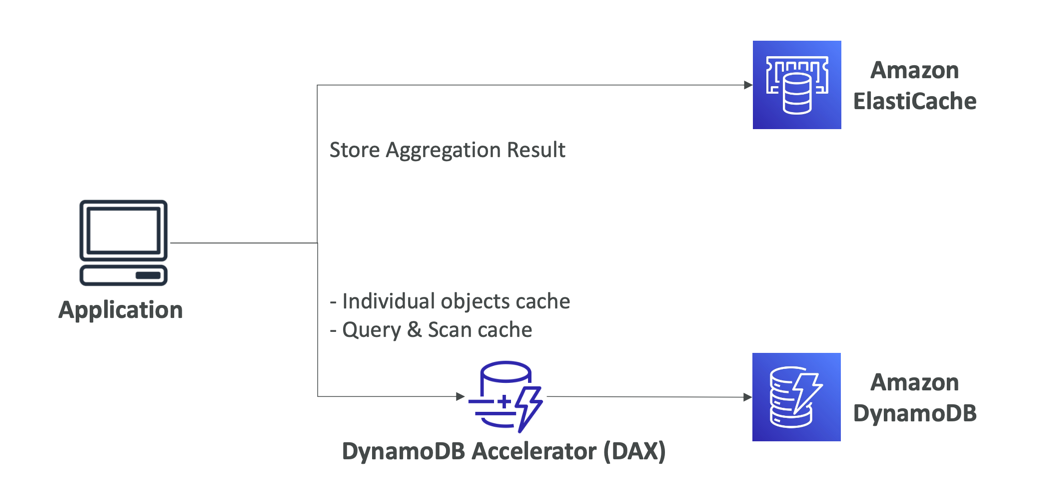
DynamoDB Accelerator - DAX
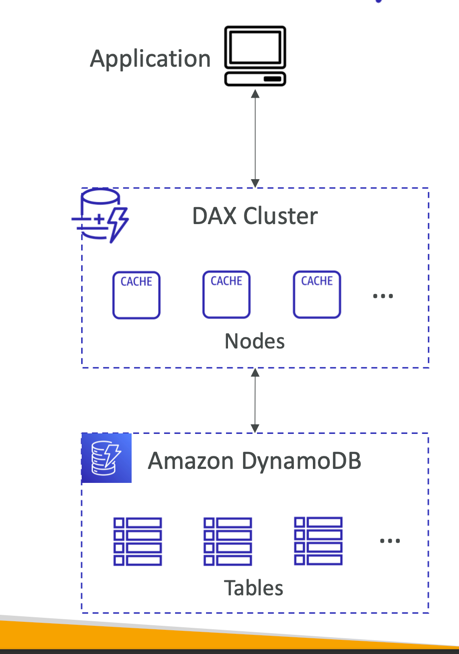
- Fully-managed, highly available, seamless in- memory cache for DynamoDB
- Help solve read congestion by caching
- Microseconds latency for cached data
- Doesn’t require application logic modification(compatible with existing DynamoDB APIs)
- 5 minutes TTL for cache (default)
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) vs. ElastiCache
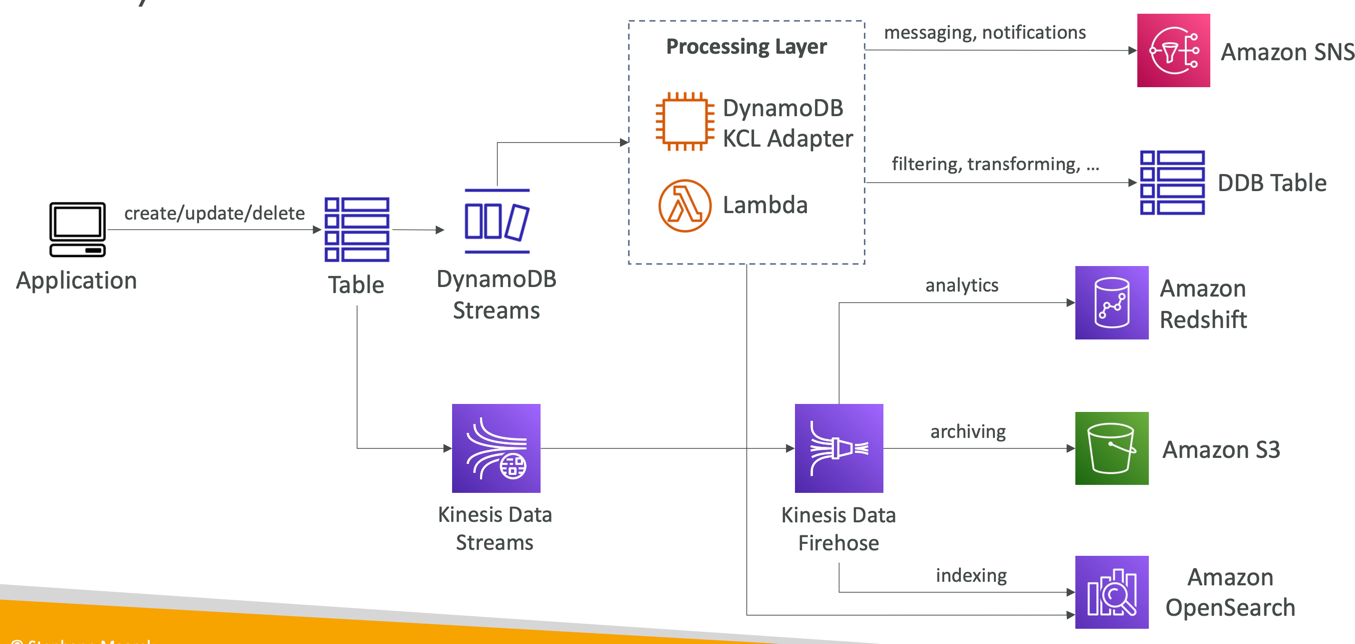
DynamoDB – Stream Processing
- Ordered stream of item-level modifications (create/update/delete) in a table
- Use cases:
- React to changes in real-time (welcome email to users)
- Real-time usage analytics
- Insert into derivative tables
- Implement cross-region replication
- Invoke AWS Lambda on changes to your DynamoDB table
DynamoDB Streams
- 24 hours retention
- Limited # of consumers
- Process using AWS Lambda Triggers, or DynamoDB Stream Kinesis adapter
Kinesis Data Streams (newer)
- I year retention
- High # of consumers
- Process using AWS Lambda, Kinesis Data Analytics, Kineis Data Firehose, AWS Glue Streaming ETL...
DynamoDB Streams
DynamoDB Global Tables
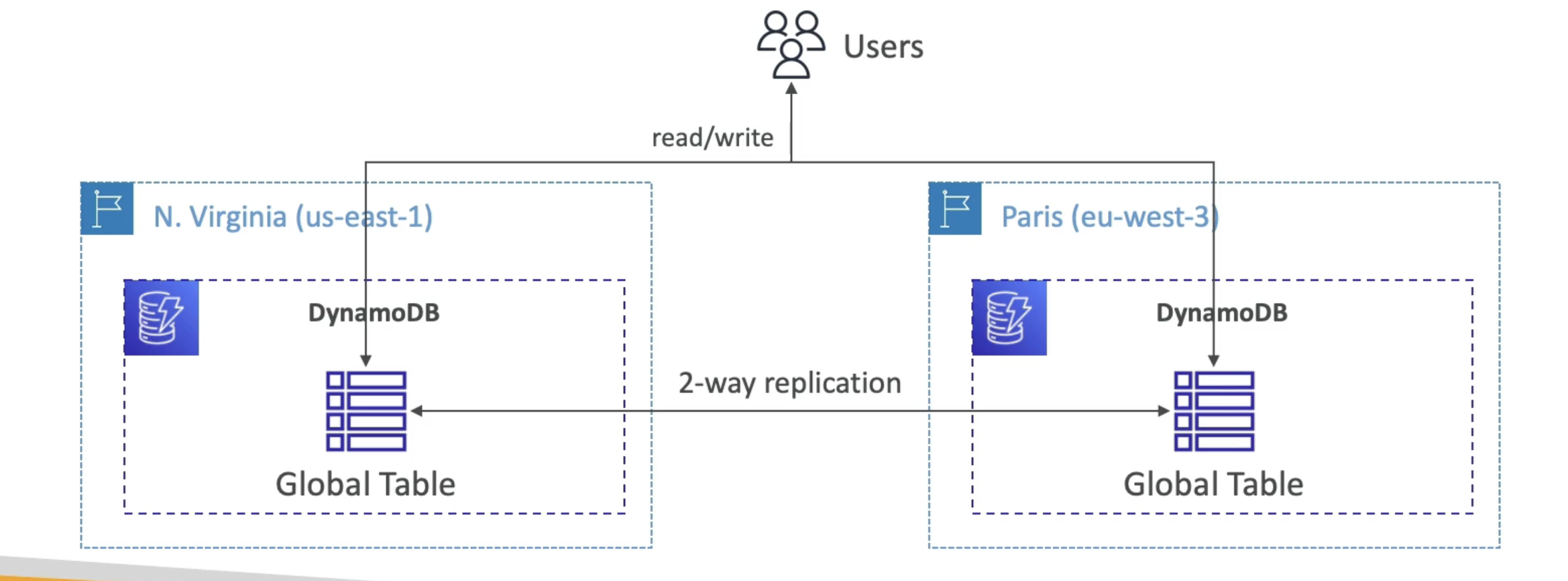
- Make a DynamoDB table accessible with low latency in multiple-regions
- Active-Active replication
- Applications can READ and WRITE to the table in any region
- Must enable DynamoDB Streams as a pre-requisite
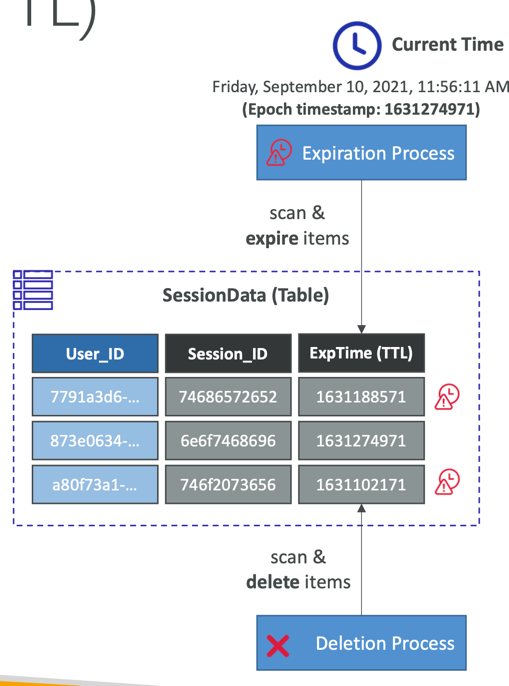
DynamoDB – Time To Live (TTL)
- Automatically delete items after an expiry timestamp
- Use cases: reduce stored data by keeping only current items, adhere to regulatory obligations, web session handling…
DynamoDB – Backups for disaster recovery
- Continuous backups using point-in-time recovery (PITR)
- Optionally enabled for the last 35 days
- Point-in-time recovery to any time within the backup window
- The recovery process creates a new table
- On-demand backups
- Full backups for long-term retention, until explicitely deleted
- Doesn’t affect performance or latency
- Can be configured and managed in AWS Backup (enables cross-region copy)
- The recovery process creates a new table
DynamoDB – Integration with Amazon S3
- Export to S3 (must enable PITR)
- Works for any point of time in the last 35 days
- Doesn’t affect the read capacity of your table
- Perform data analysis on top of DynamoDB
- Retain snapshots for auditing
- ETL on top of S3 data before importing back into DynamoDB
- Export in DynamoDB JSON or ION format
- Import from S3
- Import CSV, DynamoDB JSON or ION format
- Doesn’t consume any write capacity
- Creates a new table
- Import errors are logged in CloudWatch Logs